1781
William Herschel discovers "Georgium Sidus" (Uranus).
William Herschel discovers "Georgium Sidus" (Uranus).
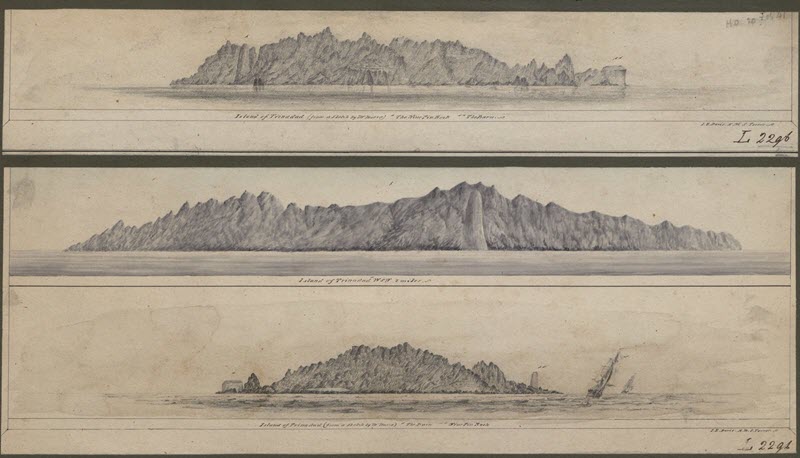
Philippe d'Auvergne leads an unsuccessful expedition to accurately chart the island of Trinidade for possible settlement. The expedition is rescued in December 1782.
The first hot air balloon flight by the Montgolfier brothers sparks a ballooning craze in Europe.
The Baseline Survey calculates the distance between Dover and Calais, an important step in cartographic science.
The King George's Sound Company is formed to exploit the maritime fur trade.
Lapérouse explores the Pacific, intending to claim Australia for France, but arrives after a British colony has been established. He disappears after disembarking from Port Jackson (Sydney).
Nathanael Portlock leads a circumnavigation of the globe.
British Prime Minister William Pitt (the younger) approves the establishment of a penal colony in Australia.
The London Committee for the Abolition of Slavery is established.
Captain Arthur Phillip and the first fleet sail from Spithead to found the Australian settlement at Port Jackson.

William Bligh leads his first (unsuccessful) breadfruit voyage on the Bounty, with the aim of transporting breadfruit plants to the Caribbean, in an attempt to establish the crop as a basis for slaves' diets. Following a mutiny, he is forced to navigate a small from Otaheite to Timor (a distance of 3618 miles). The mutineers, led by Fletcher Christian, establish a settlement on Pitcairn Island.
The Polish naturalist Anton Pantaleon Hove embarks upon an expedition to India.
Joseph Banks founds the Association for Promoting the Discovery of the Interior parts of Africa (Alternatively known as the Africa Association).
The French Revolution breaks out.
Alexander Mackenzie of the North West Company descends the Grand River to the Arctic Ocean.
Malaspina charts the coast of South America from Brazil to Tierra del Fuego
Dionisio Alcalá Galiano leads an expedition to the west coast of North America, which circumnavigates Vancouver Island.
Spanish ships capture British fur trading vessels at Nootka Sound, precipitating the Nootka Crisis.
An expedition led by George Vancouver explores the Northwest coast of North America.

Sierra Leone falls under British control.
Lord MacCartney leads Britain's first unsuccessful diplomatic mission to China.
Mackenzie completes the first crossing of North America.
Mungo Park explores the Senegal and Gambia rivers on behalf of the Africa Association.
The French East India Company is wound up.
The Royal Navy establishes the Hydrographic Office to chart the world's oceans.
Britain captures the Cape Colony, which is subsequently returned to the Dutch in 1803.
France occupies Santo Domingo.
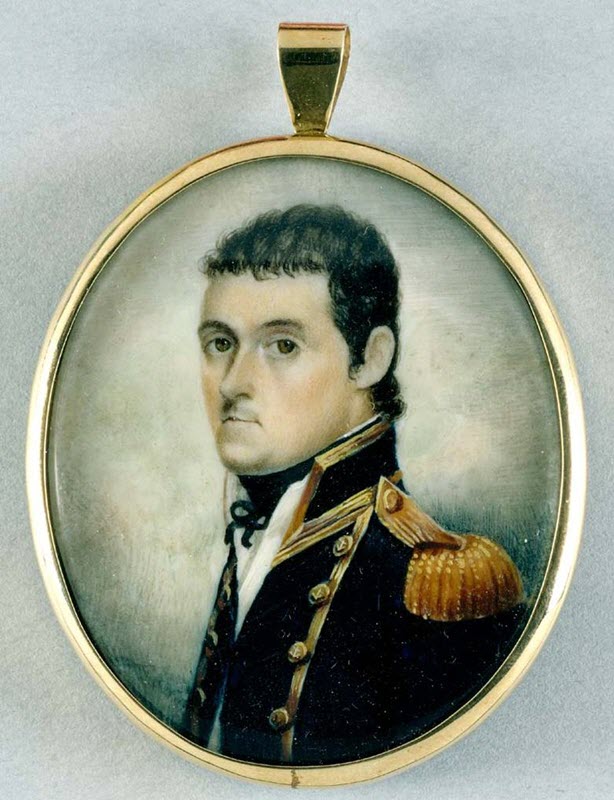

Matthew Flinders explores the Australian coast aboard the Norfolk and the Resistance.
The VOC declares bankruptcy.
British forces occupy the coast of Sri Lanka.
The Porpoise sails for Australia with George Suttor and his "garden", assembled by Banks to rectify the lack of Fruit trees in the colony. The vines form the foundation of the Australian wine industry.
Humboldt and Bonpland explore the Andes and Amazon, climbing Mount Chimborazo and discovering the north-flowing Humboldt current on the west coast of South America.
Robert Fulton designs the Nautilus, the first successful submarine.
The Great Trigonometrical Survey of India is founded.
Alessandro Volta invents an electric battery.
Flinders completes the first circumnavigation of Australia aboard the Investigator, compiling accurate coastal charts.
The Peace of Amiens temporarily ends the conflict between Britain and France.
War resumes between France and a coalition of European Powers (Britain, the Holy Roman Empire, Russia, Naples, Sicily and Sweden.)
Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of France, sells France's remaining American possessions to the United States.
An expedition led by Nicolas Baudin surveys the coast of New South Wales.
Matthew Flinders is forced to put in at Mauritius, and is imprisoned by the French for 7 years.
Adam Johann von Krusenstern leads the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe.
Meriwether Lewis and William Clark cross North America, following the Missouri River and traversing the Rocky Mountains.
Nelson achieves a decisive victory against the French and Spanish fleets at Trafalgar.
Mungo Park leads a second expedition to chart the Niger, which ends in disaster.
Britain re-occupies the Cape Colony after Napoleon invades the Netherlands.
Napoleon issues an edict prohibiting British shipping from European ports.
The Slave Trade Act abolishes the slave trade in the British Empire.
Santo Domingo is returned to Spanish control.
Mexico declares independence from Spain.
The Chilean War of Independence is fought.
David Thompson of the North West Company navigates the Columbia River.
Venezuela declares independence from Spain, which is secured in 1823.
Freycinet's map of Australia is published.
Gregory Blaxland leads the first successful crossing of the Blue Mountains (by westerners) in New South Wales.
The Cape Colony is ceded to Britain in return for a cash payment.
Napoleon is removed from power and exiled to Elba, only to escape and return to France. However, his 'Hundred Days' end in defeat at the Battle of Waterloo.
An expedition led by Otto von Kotzebue reaches Cape Krusentern, Alaska.
Allan Cunningham begins collecting plants for Joseph Banks in New South Wales.
Argentina declares independence from Spain, which is secured by 1826.
Louis de Freycinet leads a circumnavigation of the world aboard the Uranie, recording a wealth of scientific data and specimens.
Johann Baptist von Spix and Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius explore the Amazon and Negro rivers.
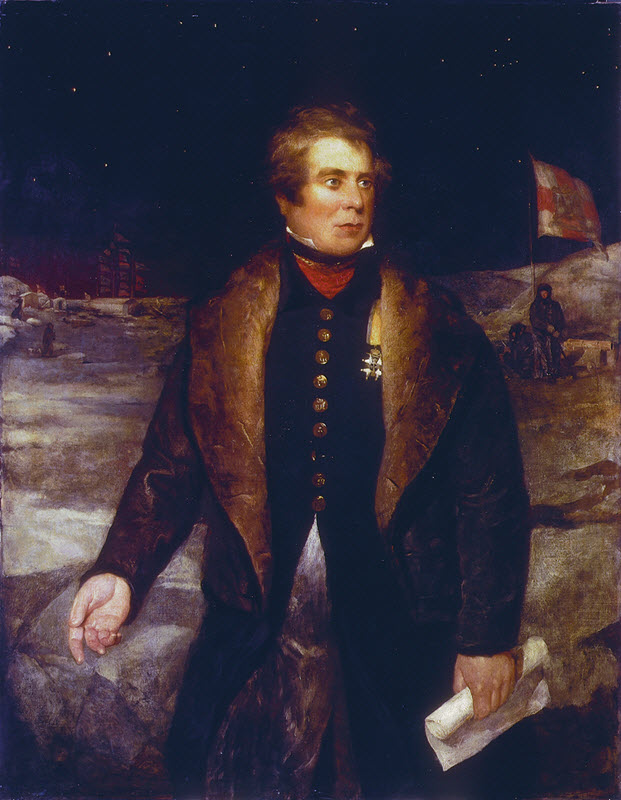

John Ross leads an expedition to the Arctic, and records that Lancaster Sound is blocked by ice.
John Franklin attempts to complete the Northwest Passage overland, travelling via the Great Slave Lake.
An expedition under William Parry travels half of the distance from Greenland to the Bering Strait, reviving hopes that a Northwest Passage may exist.
An expedition led by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen circumnavigates Antarctica.
An expedition led by William Bransfield sights Antarctica.
Ferdinand von Wrangel leads an expedition which explores the Siberian coastline, establishing that an open sea exists north of the Kolyma River. The expedition records a great deal of scientific and ethnographic data.
Peru declares independence from Spain.
Simon Bolivar assumes the Presidency of Gran Colombia, comprising Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Venezuela and Northern Peru.
The North West Company is incorporated into the Hudson's Bay Company.
Brazil declares independence from Portugal.
Nicéphore Niépce is believed to have created the world's first permanent photographic image.
Benjamin Morrell claims to have sighted land, dubbed New South Greenland, in what is now known as the Weddell Sea.
James Weddell enters Antarctic waters.
George Byron, 7th Baron Byron, leads an expedition to the Pacific.
John Franklin and William Parry lead a search for the Northwest Passage.

Frederick William Beechey leads an expedition to the Pacific and the Bering Strait, accompanied by Edward Belcher as surveyor.
Jules Dumont d'Urville leads a circumnavigation of the globe aboard the Astrolabe (formerly La Coquille), which undertakes a number of scientific surveys and locates the site of La Pérouse's shipwreck.
William Parry leads an unsuccessful attempt to reach the North Pole from Spitsbergen.
Uruguay, occupied by Portuguese and later Brazilian forces since 1816, becomes an independent state under the Treaty of Montevideo.
Britain claims the entire Australian continent as its territory.
John Ross leads a search for the Northwest Passage. Forced to abandon ship, his crew are rescued by the Isabella.
William Parry establishes the location of the Magnetic North Pole.
The July Revolution in France sees Charles X, King of France and Navarre, replaced by his cousin Louis Philippe, King of the French.
The Southern Ocean expedition under the command of Captain John Biscoe locates new sealing grounds, Adelaide Island and the Biscoe Islands, circumnavigating the Antarctic continent.
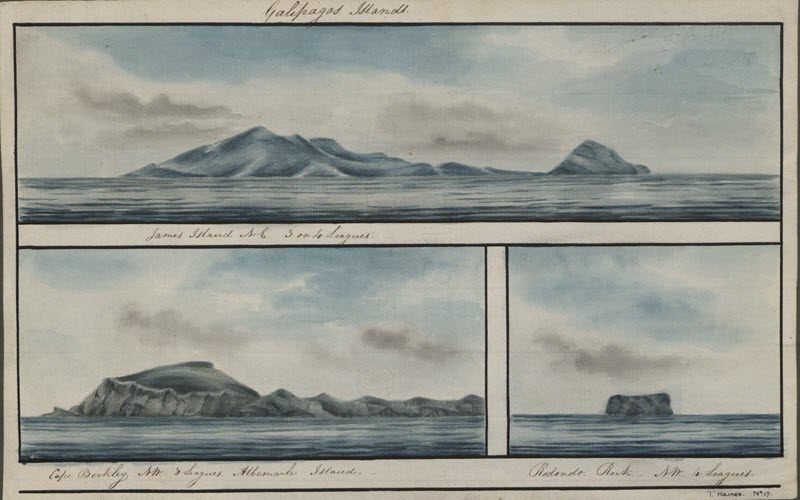

HMS Beagle carries out a second hydrographical survey of South America. The ship's supernumerary geologist, Charles Darwin, spends the voyage carrying out research which inspires his On the Origin of Species.
Robert Brown discovers the cell nucleus.
The East India Company's monopoly of trade with India is ended.
The British Parliament passes the Abolition of Slavery Act.
The Council of the Indies is abolished.
Samuel Morse invents Morse Code.
Sir George Back leads an unsuccessful attempt to discover the Northwest Passage aboard HMS Terror, which is left icebound for 10 months.
HMS Sulphur, commanded by at first by Frederick Beechey, subsequently by Henry Kellet and Edward Belcher, surveys the western coasts of America and the harbour at Hong Kong. The vessel also participates in the war with China.
Sir John Franklin serves as Governor of Van Diemen's Land (Tasmania).
Dumont d'Urville leads a second circumnavigation of the globe aboard the Astrolabe.
Charles Wilkes leads United States Exploring Expedition, a scientific voyage which reaches a series of Pacific Islands and the Antarctic.

James Clark Ross leads an expedition which charts the Antarctic coastline, discovering the Ross Ice Shelf and Transantarctic Mountains. The expedition, considered to be the last major voyage of exploration made entirely under sail, infers the position of the Magnetic South Pole; Joseph Hooker, who accompanied the crew, makes a number of important botanical and zoological observations.
The First Opium War is fought between Britain and China.