1845 - 1847
Sir John Franklin leads an expedition to the Arctic, which becomes known as the Lost Expedition. The entire complement perishes; Franklin's fate is not established until 1857.

Sir John Franklin leads an expedition to the Arctic, which becomes known as the Lost Expedition. The entire complement perishes; Franklin's fate is not established until 1857.
The Oregon Treaty is signed between Britain and the US, setting the US-Canadian boundary at the 49th parallel except for Vancouver Island.
John Rae and John Richardson lead a predominantly overland search for Franklin.
James Clark Ross leads an expedition in search of Franklin.
Slavery is abolished in the French Empire.
The McClure Arctic Expedition, launched in the hope of determining Franklin's fate becomes icebound, and its crew are forced to trek overland to escape. McClure becomes the first person to traverse the Northwest Passage, utilising both ship and sledge.
Horatio Thomas Austin leads an expedition to find Franklin.
The First Grinnell Expedition, an American attempt to find Franklin, led by Edward De Haven, is launched under the sponsorship of the merchant Henry Grinnell. In conjunction with British missions to the Arctic, the expedition discovers a number of sites associated with the doomed Franklin.
Sir Edward Belcher leads a search for Franklin, which conducts a number of surveys of the Arctic region.

Dr Elisha Kent Kane leads the Second Grinnell Expedition to the Arctic, which fails to find further traces of Franklin's Lost Expedition, and becomes stuck in ice.
An Arctic Expedition under Francis McClintock establishes the fate of Franklin's Lost Expedition.
The Indian Rebellion of 1857, alternatively known as the Indian Mutiny and India's First War of Independence, is fought.
The East India Company is abolished.
Charles Darwin publishes On the Origin of the Species by Natural Selection.
The Suez Canal is built, significantly shortening shipping routes between Europe, Asia and Australasia.
Isaac Israel Hayes leads an expedition to the North Pole, which (erroneously) claims to have reached the farthest north point of any human endeavour. Hayes also claims to have seen fictional Polar Sea reported by Kane in 1855.
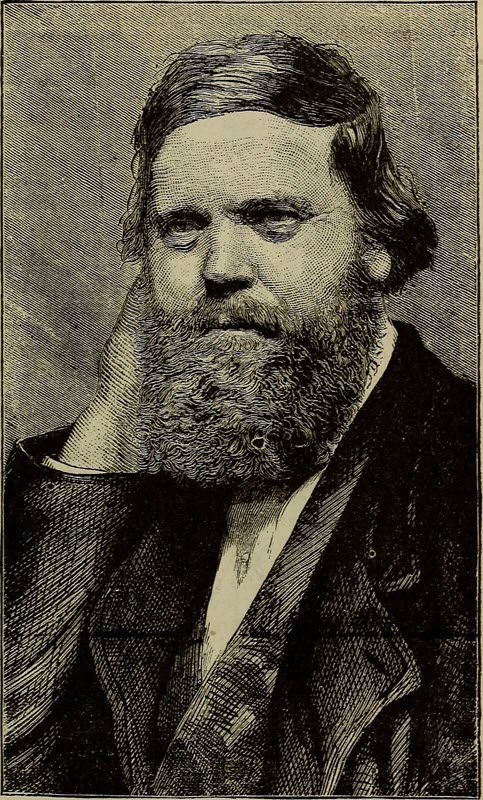

Charles Francis Hall leads an American expedition to seek information about Franklin's fate, also encountering relics of Frobisher's expeditions.
The American Civil War is fought between the United States of America and the rebel Confederate States.
France acquires Cochin-China.
Hall leads a second expedition to the Arctic, establishing that members of the Franklin starved to death.
The Constitution Act establishes self-government for the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
The Polaris Expedition, an unsuccessful American attempt to reach the North Pole is led by Charles Francis Hall, who dies after an exploratory sledging expedition.
George Strong Nares leads the Challenger Expedition, a voyage of almost 70,000 miles, which collects a vast quantity of geographical, oceanographic and scientific data.
The Austro-Hungarian North Pole expedition discovers Franz Josef Land.
British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli authorises the purchase of shares in the Suez Canal Suez Canal from the Khedive of Egypt.
The Howgate Polar Expedition seeks to establish relations between the United States and Inuit peoples, and establish settlements in the Arctic. The expedition is a failure, and it transpires that Howgate had embezzled vast sums of government money.
The Vega Expedition, led by Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, successfully traverses the Northeast Passage; the voyage also comprises the first successful circumnavigation of Eurasia.
The Jeannette Expedition, officially the United States Arctic Expedition, fails to reach the North Pole via the Bering Strait. 20 of the 33 expedition members die in an attempt to reach the Lena Delta after the USS Jeanette is crushed by ice.
The Lady Franklin Bay Expedition, officially the International Polar Expedition, is launched in an attempt to record scientific data in the Arctic. Expedition members achieve a farthest north record, but only 7 of the 25 men survive after attempts to re-provision the mission are abandoned.
The First International Polar Year, a co-ordinated attempt to record scientific data in the Arctic, is carried out.
Robert E. Peary unsuccessfully attempts to cross Greenland.
Peary leads an expedition to Greenland, establishing that Greenland is an island rather than a peninsula.
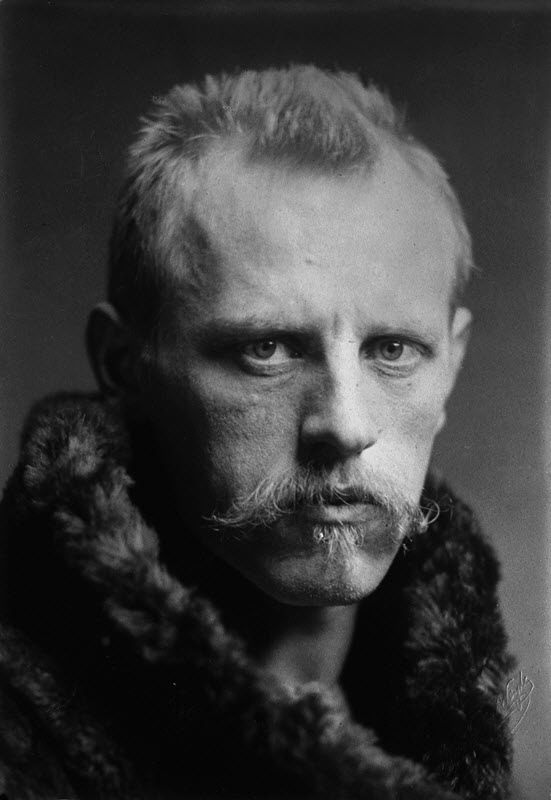

Fridtjof Nansen’s Fram Expedition attempts to reach the North Pole by deliberately becoming locked in drifting ice.
Frederick Cook leads the Miranda Expedition, which explores the western coast of Greenland. Cook navigates an open boat across 90 miles of open sea to secure help when the ship Miranda encounters trouble.
S. A. Andrée's attempt to reach the North Pole by hot air balloon ends in disaster.
The Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Adrian de Gerlache, and including Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen, becomes the first to overwinter on an Antarctic ice shelf.
The British Antarctic Expedition, led by the Anglo-Norwegian explorer Carsten Borchgrevink, is the first to overwinter on the Antarctic mainland.
Walter Wellman leads an expedition through Franz Josef Land.
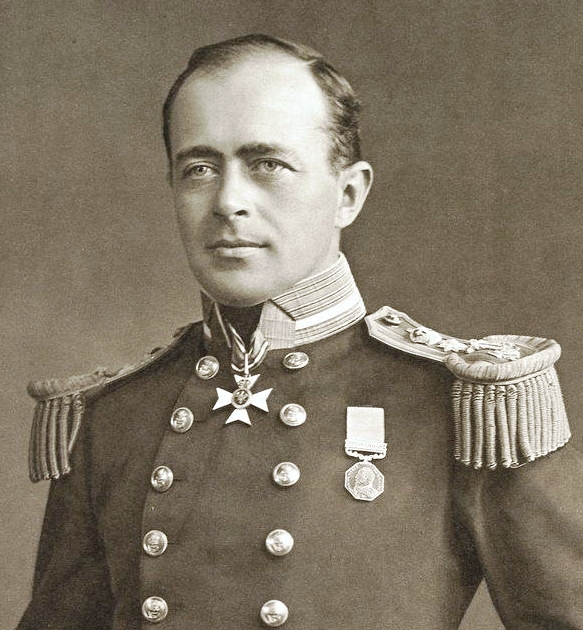

The National Antarctic Expedition led by Robert Falcon Scott discovers the Polar Plateau.
The Gauss Expedition - the first German-organised Antarctic expedition - explores Eastern Antarctica, making a scientific survey of Heard Island.
The Swedish Antarctic Expedition, led by Otto Nordenskjöld (nephew of Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld) explores the eastern coast of Graham Land, collecting a variety of specimens. A relief expedition becomes stuck in pack ice, and the two groups are rescued by an Argentine Navy vessel.
The Scottish National Antarctic Expedition establishes a permanent weather station in the South Orkney Islands, discovers new land east of the Weddell Sea, and collects a large quantity of scientific specimens.
Orville and Wilbur Wright successfully test an aeroplane at Kittyhawk, North Carolina.
Anthony Fiala leads the Ziegler Polar Expedition, a failed attempt to reach the North Pole. The stranded party is rescued by a mission led by William S. Champ.
The Third French Antarctic Expedition attempts to relieve the stranded Nordenskiöld party, and explores the islands and coast of Graham Land. It names Loubet Land after President Emile Loubet.
Roald Amundsen leads the first successful passage of the Northwest Passage by boat.
Auguste and Louis Lumiere develop colour photography.
The British Antarctic Expedition, led by Ernest Shackleton, reaches the magnetic South Pole.
The Fourth French Antarctic Expedition, led by Jean-Baptiste Charcot, charts the Bellingshausen Sea and surrounding area.

Robert Peary leads an expedition which claims to have reached the North Pole.
Roald Amundsen leads the first expedition to reach the South Pole, beating the ill-fated Scott expedition by a matter of days.
The Japanese Antarctic Expedition explores King Edward VII Land.
The privately-funded Terra Nova Expedition, led by Robert Falcon Scott, travels to the Antarctic to carry out scientific experiments and attempt to reach the South Pole. A five-man team reaches the Pole 34 days after Amundsen's expedition, but perishes on the return journey.
Douglas Mawson leads the Australasian Antarctic Expedition, an attempt to chart the coastline of Antarctica. Mawson and six others are stranded on Cape Denison between February and December 1913, when the Aurora leaves without them, and is unable to turn back.
The Second German Antarctic Expedition enters the Weddell Sea, and becomes trapped in pack ice. The expedition investigates whether the supposed New South Greenland exists, concluding that it was a mirage.
Knud Rasmussen and Peter Freuchen prove that Greenland and Peary Land are not separated by a channel, by travelling across Greenland by dogsled. The expedition is the first of seven led by Rasmussen from the settlement of Thule, known as the Thule Expeditions.
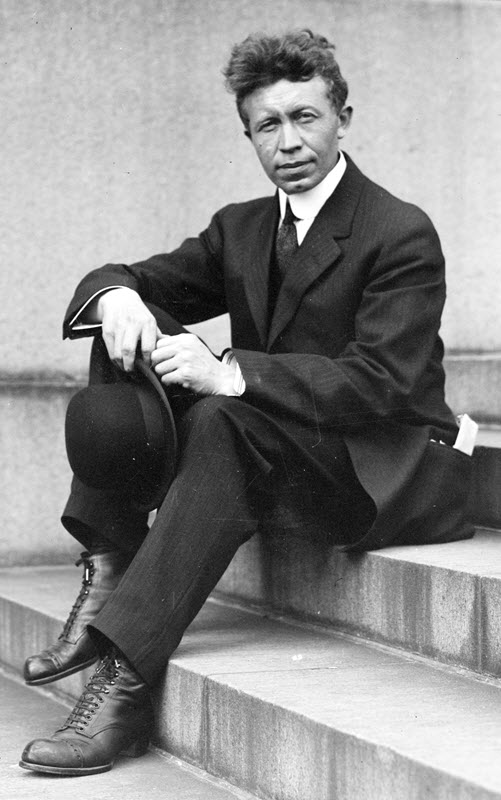

The Canadian Arctic Expedition, led by Vilhjalmur Stefansson, discovers a series of previously unknown islands and makes a series of scientific observations; however, eleven lives are lost aboard the expedition's principal ship, the Karluk, which is carried away and crushed by ice.
The Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, led by Ernest Shackleton, fails in its attempt to cross the Antarctic; Shackleton leads a successful attempt to secure help from South America after sailing to South Georgia in an open boat. The supporting Ross Sea party, which lays a series of supply depots for the expedition, suffers three deaths including that of its leader Aeneas Mackintosh.
The First World War is fought.
The Russian October Revolution brings the Russian Empire to an end.
Roald Amundsen traverses the Northeast Passage aboard the Maud.
Rasmussen leads the Fifth Thule Expedition, an investigation into the ethnography, archaeology and anthropology of the Inuit peoples. In completing the expedition, he becomes the first European to cross the Northwest Passage by dogsled.
Shackleton dies on South Georgia whilst leading the Shackleton-Rowett Expedition (also known as the Quest Expedition) to the Antarctic.
Edwin Hubble proves the existence of other galaxies.