1492 - 1493
Christopher Columbus leads his first voyage to the Indies, intending to reach Japan by a Western route.
Christopher Columbus leads his first voyage to the Indies, intending to reach Japan by a Western route.
Columbus' second voyage reaches the Leeward Islands, Jamaica, Puerto Rico and Hispaniola.
Columbus brings sugar cane to the Americas, where it grows easily. This marks the foundation of the sugar industries in Jamaica, Haiti and Cuba.
A Spanish colony is established at Santo Domingo in Hispaniola.
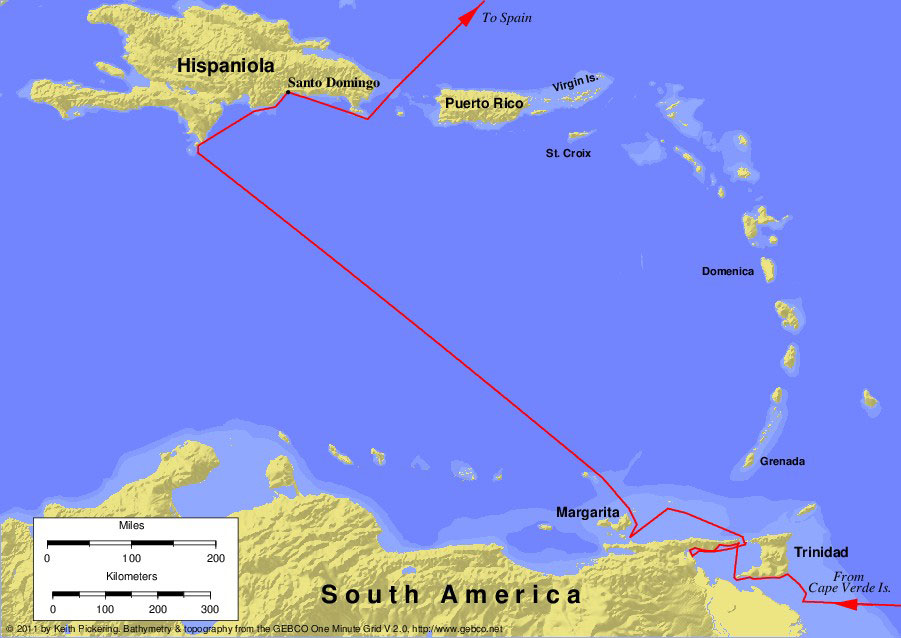
Columbus' third voyage reaches contemporary Trinidad, Tobago, Venezuela and Hispaniola.
Columbus' fourth voyage reaches contemporary Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Cuba, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama.
A Spanish colony is established on Jamaica.
Spanish colonisers establish coffee, sugar and tobacco plantations on Cuba.
Juan Ponce de Leon sails from Puerto Rico and is the first European to reach the Gulf Stream.
The Spanish cultivate tobacco in San Domingo.
Bartolomé de las Casas' Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies is published.
John Hawkins enslaves people in the place we now know as Sierra Leone and transports them to the Caribbean.

Francis Drake embarks upon a series of voyages to the West Indies, intended to disrupt and capture Spanish shipping.
Francis Drake captures a Spanish treasure ship carrying 26 tons of silver and 80 lbs of gold.
Anglo-Spanish War breaks out following the capture of English merchant ships in Spanish harbours. Though much of the conflict took place in Europe, England launched repeated expeditions against Spanish territories in the New World.
Ginger grown in Jamaica is imported into Europe.
Spanish colonists establish a colony on Trinidad.
An English colony is established on the island of St Lucia. The indigenous Kalinago resist the colonisation and drive off the colonists.
England establishes a colony in Virginia. Due to prevailing trade winds, the Caribbean becomes an important stopping point for ships sailing to the new colony.
A flotilla travelling to Jamestown is struck by a storm. One ship is stranded at Bermuda, perhaps inspiring William Shakespeare's The Tempest. Its passengers establish a colony on the island before sailing on to Jamestown.
British colonists attempt to colonise Grenada. They are driven off the island by the indigenous Kalinago.
Bermuda is incorporated into the charter of the Virginia Company. A permanent colony is established at St George.
First record of Dutch colony on Tortola.
Operation of the colony at Bermuda is passed to the Somers Isles Company.
Essequibo is colonised by Dutch traders.
A colonial parliament, the House of Assembly, is created to govern the colony at Bermuda.
An English colony is established on the island of St Christopher (St Kitts).
Spanish forces sack the Dutch colony on Tortola.
A French colony is established on St Kitts.
English and French colonists from St Kitts establish a colony on Tortuga, off the coast of Hispaniola.
English and Dutch colonists establish colonies on St Croix. Disputes between the colonies lead the Dutch colonists to abandon the island.
A joint force of British and French colonists on St Kitts massacre a significant number of the indigenous Kalinago.
Henry Powell lands on Barbados with a party of 80 colonists and 10 enslaved people to establish a colony.
Berbice is colonised by the Dutch West India Company.
Colonists from St Kitts establish a colony on Nevis.
Dutch colonists attempt to establish a colony on Tobago, but are driven off by the Indigenous population and attacks by Kalinago from Grenada and St Vincent.
An English colony is established on Providence Island.
The English and French colonies on St Kitts and Nevis are destroyed by Spanish forces. The colonies return following the Spanish departure in 1630.
The French and English colonies on Tortuga are sacked by Spanish forces.
The English colony on St Croix is sacked by Spanish forces.
English and French colonists make a second attempt to establish colonies on Tortuga. The island becomes an important base for buccaneers.
Colonists from St Kitts establish a colony on Antigua.
Predominantly Irish colonists from St Kitts establish a colony on Montserrat.
Dutch forces occupy the Spanish colony of Curaçao.
A French colony is established on Martinique.
A French colony is established on Guadeloupe.
A Spanish attack on the English colony on Providence Island is repelled.
Spanish forces sack the English and French colonies on Tortuga.
A Dutch colony is established on St Eustatius. The island changes hands some 21 times between the 17th and 19th centuries.
The legal basis for slavery is established by statute in Barbados.
English colonists attempt to establish a colony on Tobago, but are ousted by the indigenous population.
Spanish forces occupy Tortuga.
English colonists make a second attempt to colonise St Lucia. This colony is again repulsed by Kalinago.
A locally elected House of Assembly is formed in Barbados.
The colony on Providence Island is sacked by Spanish forces.
English slave traders begin importing enslaved people to Barbados.
French forces take possession of Tortuga.
English Civil War.
The first sustained European colony on Tobago is established by Courlanders from modern-day Latvia.
English colonists return to St Croix.
English colonists from Bermuda establish a colony in the Bahamas, on the island of Eleuthera.
A French colony is established at Saint-Barthélemy.
A French colony is established at Grenada.
Enslaved people on two plantations on Barbados rise against the slaveholders over the lack of food.
Spanish forces sack the English colony on St Croix. The island passes to French control and is subsequently ceded to the Knights of Malta.
An English colony is established in Suriname.
Colonists from St Kitts establish a colony on Anguilla.
As Barbados is controlled by Royalists, Parliament issues an act halting all trade with the island.
The Navigation Acts restricted the use of foreign ships in trade between Britain and her colonies.
Saint-Barthélemy is administered by the Knights of Malta.

Barbados, held by Royalist forces, is captured by the Parliamentarian commander, George Ayscue.
First Anglo-Dutch War breaks out as England attempts to prevent Dutch trade in English colonies.
Anglo-Spanish War. Though the war ends with the restoration of Charles II in 1660, the conflict in the Caribbean continues until the 1667 Treaty of Madrid.
Spanish forces occupy Tortuga for the final time.

The Western Design, an English expedition against the Spanish West Indies, is launched with the objective of capturing Hispaniola.
An English attack on Hispaniola is repulsed. The English forces instead turn to Jamaica, capturing the island.
Groups of enslaved people escaping from plantations in Jamaica establish settlements in the Blue Mountains and in Cockpit Country. These groups come to be called 'Maroons'.
The Dutch take control of Tobago.

Restoration of Charles II.
France and England agree not to colonise Dominica and St Vincent, islands occupied by Kalinago.
French colonists agree a treaty with the Indigenous peoples of St Lucia, allowing the French to establish a colony on the island.
A second Navigation Act is passed to promote English commerce and protect it from European competition in colonial trade.
The Royal African Company is founded and is given a monopoly over the British slave trade.