
1660
Restoration of Charles II.

Restoration of Charles II.
France and England agree not to colonise Dominica and St Vincent, islands occupied by Kalinago.
French colonists agree a treaty with the Indigenous peoples of St Lucia, allowing the French to establish a colony on the island.
A second Navigation Act is passed to promote English commerce and protect it from European competition in colonial trade.
The Royal African Company is founded and is given a monopoly over the British slave trade.
Humphrey Walrond, the governor of Barbados, creates the 'Slave Code', establishing a basis for slavery. A simultaneous piece of legislation provided rights and privileges for white servants.
A proclamation is issued which grants the free population of Jamaica the rights of English citizens.
Militia formed in Jamaica.

Rum distillation begins in Barbados.
Thomas Modyford introduces the 'Slave Code' to Jamaica.
A House of Assembly is established at Jamaica.
English forces occupy St Lucia. The island is ceded back to France in the Treaty of Breda in 1667.
Second Anglo-Dutch War. France enters the war in 1666, on the Dutch side.
Dutch colonists on Tortola are attacked by British privateer, John Wentworth.
French forces occupy St Kitts and Antigua.
French control of St Croix. The island is abandoned in 1696.
A Danish colony is established on St Thomas.
The Battle of Nevis sees a clash between an English squadron and an allied Franco-Dutch fleet. An English victory prevented the invasion of the island.
French forces occupy Montserrat. The island is returned to English control in the Treaty of Breda.
Dutch forces capture the English colony in Suriname.

A British fleet under the command of Admiral Sir John Harman attacks and destroys a French mercantile fleet at anchor in Martinique, virtually wiping out the French trade in the Caribbean.
An invasion of Anguilla leads the colonists to evacuate to Antigua.
Jamaica becomes the world's largest exporter of sugar.
As part of the Treaty of Madrid, Spain recognises English possessions in the Caribbean and permits the establishment of logwood cutting stations along the Yucatan coast.
Louis XIV endorses the transport of enslaved people from Africa to Saint-Domingue to work on sugar plantations.
The Bahamas become a proprietary colony.
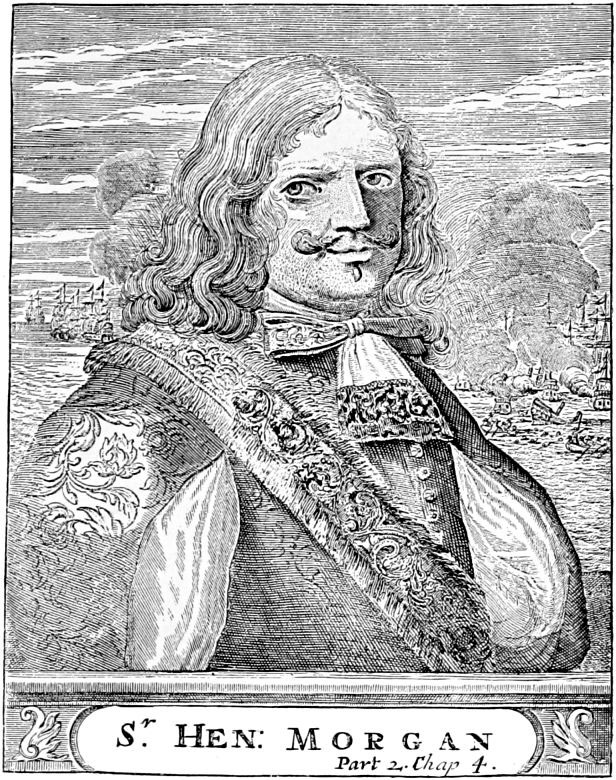

Welsh privateer Henry Morgan captures and loots Panama.
The Royal African Company is reformed with a broader charter.
Third Anglo-Dutch War. England and France join forces against the Netherlands.
England takes control of the territories which now form the British Virgin Islands.
The first enslaved peoples resistance movement takes place in Jamaica when around 300 enslaved people escape the parish of St Ann and head for the mountains.

Sir Christopher Codrington establishes 'Betty's Hope', Antigua and Barbuda's first full-scale sugar plantation.
An uprising among enslaved peoples in Barbados is brutally suppressed.
Henry Morgan, the privateer who led a raid on Panama, is knighted and appointed deputy governor of Jamaica.
Grand Turk is colonised by English salt collectors from Bermuda.
Criollo cacao trees are introduced to Trinidad from Venezuela.
A conspiracy involving around 180 enslaved people is betrayed in Vere, Jamaica.
Spanish forces sack New Providence.
The Somers Isles Company, which administered the colony in Bermuda, is dissolved. Management of the colony passed over to the Crown.
The Code Noir decree is introduced to all French Caribbean colonies to define the conditions of slavery.
Prisoners from the failed Monmouth Rebellion in England are transported to the Caribbean and enslaved.
Uprisings break out on plantations in Guanaboa, Jamaica.
The Nine Years War sees England, Spain and other European powers pitted against France.
French forces occupy St. Kitts.
English forces occupy St. Kitts.
Around 400 enslaved Koromanti in the parish of Clarendon in Jamaica burn Sutton's Plantation and escape to the hills.
British forces briefly occupy Saint-Barthélemy, deporting the French colonists and leaving the island unoccupied.
Unsuccessful English attempt to seize Guadeloupe.
An alleged plot to take over Barbados is uncovered and the leaders identified as Hammon, Ben, and Sambo. The discovery leads to over 200 arrests and almost 100 executions.
An earthquake devastates the town of Port Royal, destroying much of the harbour.
A planned rebellion among enslaved peoples in Barbados is discovered.
A French force, led by Admiral Du Casse, attacks Jamaica. Though the invasion is ultimately defeated, they succeed in damaging or destroying many sugar estates and plantations.
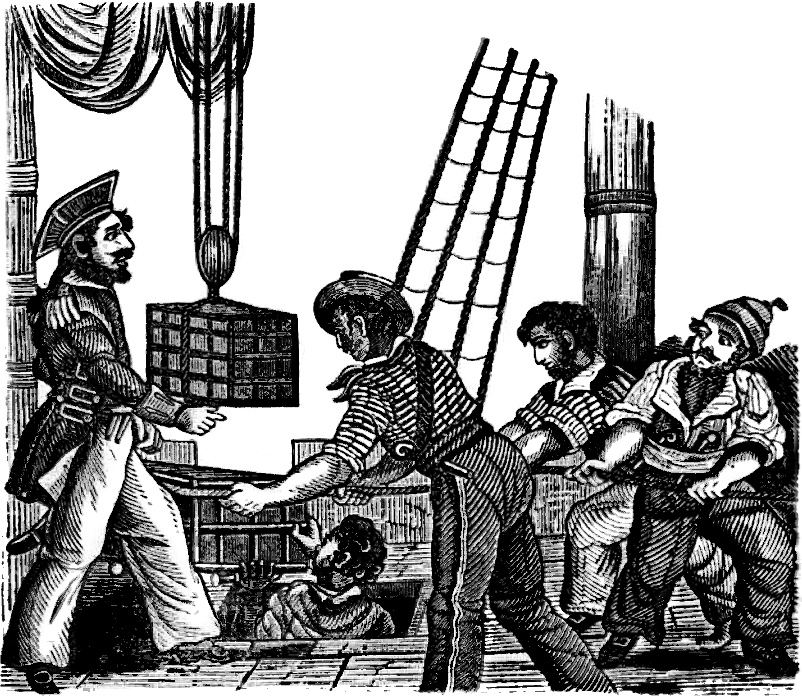
Pirate Henry Avery lands in Nassau following a successful raid on shipping in the Indian Ocean.
The Treaty of Ryswick cedes the western third of Hispaniola to France. The enlarged colony of Saint-Domingue becomes rich on the sale of sugar cane.
The Royal African Company loses its monopoly on the slave trade. It is now opened to private traders and the number of enslaved people transported by English merchants increases significantly.
Scottish colonists attempt to establish a colony on the Isthmus of Darien. A combination of disease and attacks from Spanish forces cause the colony to fail.
Spanish crown grants an asiento to the French Company of Guinea granting permission to trade in enslaved people and commodities.
English forces annex the French part of St Kitts.
War of the Spanish Succession between France, Spain, Britain, the Netherlands, Portugal and others.
Queen Anne's War, the American theatre of the War of Spanish Succession.
Spanish-French forces sack Nassau.
English forces launch an unsuccessful siege of Guadeloupe.
French forces attack St. Kitts and Nevis, bombarding and pillaging the islands.
Pirates Benjamin Hornigold, Henry Jennings and Thomas Barrow declare themselves as governors of New Providence. The so-called 'Republic of Pirates' lasts until 1718, when governor Woodes Rogers reaches the island.
A series of French attacks on Montserrat are repulsed.
A French expedition led by Jacques Cassard raids British, Dutch and Portuguese territories across the Caribbean.
Treaty of Utrecht concludes the War of Spanish Succession. Britain is ceded control over St Kitts.
South Sea Company is granted the asiento, a license to conduct the slave trade in Spanish colonies.
A Spanish treasure fleet is wrecked by a hurricane. Pirates, including Henry Jennings, launch a raid on salvagers attempting to recover gold from the wreck.
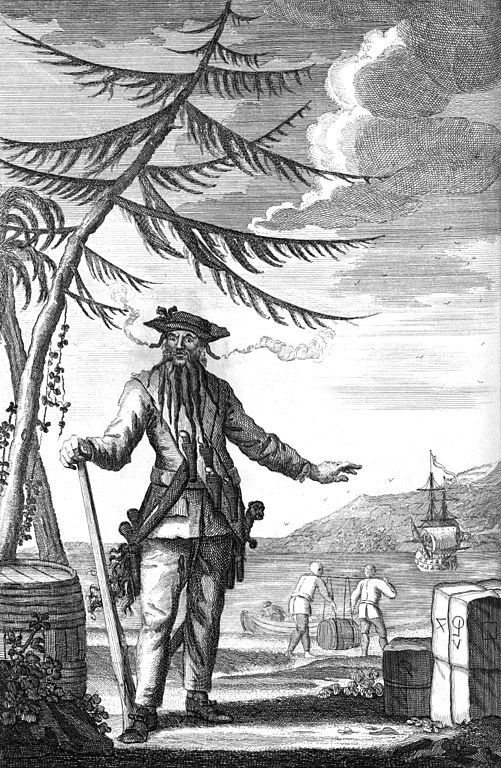

Edward Teach (Blackbeard) captures La Concorde, a French merchant vessel off, the coast of St Vincent. He made the ship his flagship, renaming it Queen Anne's Revenge.
Barbadian planter Stede Bonnet turns to piracy, purchasing a ship which he names Revenge.
Danish colonists establish a colony on St John.
Pirates operating out of Nassau, including Edward Teach (Blackbeard) and Stede Bonnet, blockade the port of Charles Town in South Carolina.

The Bahamas are made a British crown colony. The first governor, Woodes Rogers, begins to disperse the pirates who had made New Providence their home, offering a pardon to those who surrendered to British rule.
Death of notorious pirate, Edward Teach (Blackbeard).
Pirate Charles Vane makes a daring escape from the blockaded port at Nassau.
Capture, trial and execution of pirate Jack Rackham.
Trial and execution of pirate Charles Vane, who had been captured in 1719.
British colonists attempt to establish a colony at Petit Carenage in St Lucia, but are driven off by the French.
France establishes a colony on Dominica.
Criollo cacao trees are introduced to Trinidad from Venezuela.
Sarah Bassett, an elderly enslaved person in Bermuda, is burned at the stake for allegedly poisoning her owners. This was one of several ‘poisoning plots’ that took place.
Coffee is planted in Jamaica.
First Maroon War in Jamaica. Colonial forces attempt to suppress Maroon raids on plantations in Jamaica. Using guerilla tactics and superior knowledge of the terrain, the Maroons succeed in holding off the colonial attacks.
A British colony is established on the Black River on the Mosquito Coast, territory claimed by Spain.
Denmark purchases St Croix from France.
The Molasses Act places a tax on all sugar from non-British colonies, widely encouraging sugar smuggling.
Enslaved people in the Danish colony of St John occupy the fort and take control the island. The uprising lasts until 1734, when it is put down by French and British forces.
Colonial forces capture Nanny Town, the main settlement of the Windward Maroons. Many Maroons, led by Queen Nanny and Quao, successfully escape to settle elsewhere.
A planned uprising among enslaved peoples in Antigua is uncovered.
Colonial authorities in Jamaica sue for peace with the Leeward Maroons, led by Cudjoe. The Maroons won grants of land, but were required to fight on behalf of the colonial authorities against the rebels, independent Maroon communities and invading forces.
The War of Jenkin's Ear sees conflict between Britain and Spain due to disagreements over trading activities in the Spanish Caribbean.
The War of the Austrian Succession is fought in Europe, India and North America. France, Spain, Prussia and Bavaria are pitted against Britain, the Dutch Republic, Hanover and the Holy Roman Empire.
Peace is agreed with the Windward Maroons. Quao won similar terms to Cudjoe the year before, but was further required to return runaway enslaved people who had joined him in the three years prior.
The Netherlands establishes a colony in Demerara.
A group of Leeward Maroons rebel and join an enslaved peoples uprising in Jamaica. The leader of the Leeward Maroons, Cudjoe, succeeds in suppressing both uprisings.
An uprising among enslaved people in Jamaica is suppressed by the Windward Maroons.
French forces attempt to take Anguilla but are repulsed with heavy losses.
Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ends the War of Austrian Succession. As part of the terms of the treaty, Britain's control of the asiento is renewed.
Thomas Thistlewood starts a detailed diary of life on a sugar plantation in Jamaica and his interactions with enslaved people.