1685
Composer J. S. Bach is born.
Composer J. S. Bach is born.
James II crowned King of England and Scotland.
Edict of Fontainebleau outlaws Protestantism in France.
James Scott, Duke of Monmouth, attempts to overthrow James II and claim the throne in the 'Monmouth Rebellion'.
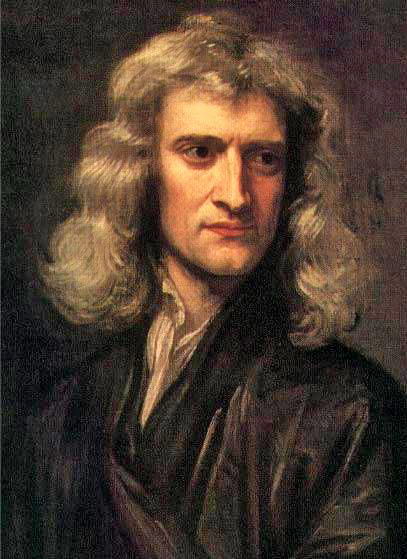

Isaac Newton expounds the theory of gravity in his 'Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica'.
Aphra Behn's 'Oroonoko: or, the Royal Slave', regarded as one of the first novels in English, is published.
The Nine Years War, between Louis XIV's France and a Grand Alliance of other European powers.
The Glorious Revolution sees James II overthrown by William of Orange.
A Bill of Rights decrees Parliamentary freedom from the Crown, and civil freedom from "cruel and unusual punishment".
Edward Lloyd's coffeehouse in London becomes a popular exchange for shipping news and insurance deals. It will later give its name to the insurance market Lloyd's of London.
Henry Purcell's opera 'Dido and Aeneas' is first performed.
Andrew Marvell publishes 'Poems on Affairs of the State'.
William III and Mary II crowned King and Queen of England and Scotland. This heralds the start of the rule of the House of Orange and Stuart.
Act of Toleration grants freedom to worship for Nonconformists.
Bill of Rights excludes Catholics from the British throne.

John Locke writes his 'Essay Concerning Human Understanding', a year after finishing 'Two Treatises of Government'.
Henry Purcell's 'King Arthur, or the British Worthy', with a libretto by John Dryden.

New East India Company formed in London.
The Salem witch trials begin in Massachusetts.
The Languedoc Canal connects the Mediterranean with the Bay of Biscay.
England creates a permanent National Debt.
The Amish religious movement is established by Jakob Ammann.
Thomas Southerne writes 'The Fatal Marriage'.
The Triennial Act establishes General Elections every three years.
Foundation of the Bank of England.
John Locke writes 'The Reasonableness of Christianity'.
The death of Henry Purcell.
Print run of 'The Flying Post; or, the Post-Master'.
Print run of 'Pax Pax Pax; or, a Pacifick Post-Boy'.
Foundation of the Board of Trade and Plantations.
The Kit-Cat Club, one of the most powerful gentlemen's clubs of the early eighteenth century, is established.

Sir John Vanbrugh writes 'The Provok'd Wife'.
Dr Thomas Bray founds the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge (SPCA).
Gilbert Burnet writes 'Exposition of the Thirty-Nine Articles'.
80% of Britain's population earn their living from the land.
Print run of 'The Edinburgh Gazette'.
Print run of the 'History of the Works of the Learned'.
Joseph Sauveur published a treatise on the vibrations of musical tones.
John Dryden writes 'Fables Ancient and Modern'.
The Deist Matthew Tindal publishes his 'Rights of the Christian Church', asserting the supremacy of the state over the church. It is widely condemned.
Jethro Tull invents the seed-drill
Anne Finch, Countess of Winchilsea, writes 'The Spleen'.
The Norwich Post, probably the first provincial newspaper, is established.
John Dunton publishes the 'Post-Angel'.
Establishment of the Daily Courant, the first daily newspaper.
Publication of 'A Pacquet from Parnassus'.
Anne crowned Queen of England and Scotland.
War of the Spanish Succession.
Isaac Newton is elected President of the Royal Society.

Jonathan Swift writes 'A Tale of a Tub'.
Isaac Newton publishes 'Opticks', in which his theories of light are discussed.
Edmund Halley correctly predicts the return in 1758 of a comet last sighted in 1682. The comet becomes known as Halley's Comet.
The German composer Johann Pachelbel dies.
The Society of Antiquaries holds its first meeting, although it will not gain a royal charter until 1751.
The 'Muse's Mercury', edited by John Oldmixon, is established.
The Acts of Union, passed by the Parliaments of England and Scotland, unites the two kingdoms to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The acts create a single parliament in London.
Isaac Watts publishes his 'Hymns and Spiritual Songs'.
Britain is still overwhelmingly rural. The population of Birmingham is approximately 8,000. The population of Leeds is approximately 7,000.
Jethro Tull's mechanical sower allows large-scale planting of seeds.
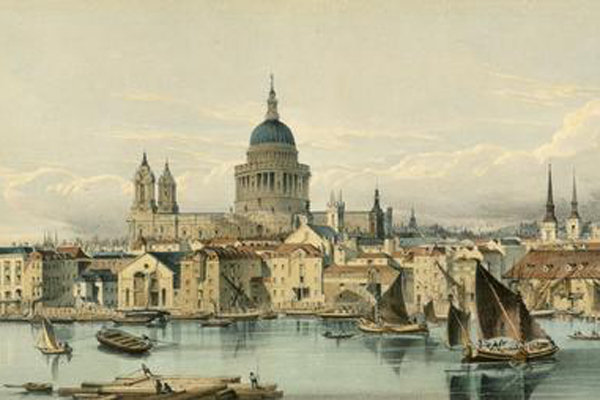
Sir Christopher Wren completes St Paul's Cathedral in London.
Matthew Tindal publishes his 'Defence of the Rights of the Christian Church'. As with his earlier work, this proves controversial. The House of Commons orders a copy of it to be burnt by the common hangman.
Sir Richard Steele publishes 'The Tatler'.
The first Copyright Act is passed.
The 'Examiner' is founded, with Jonathan Swift briefly as editor.
The 'Visions of Sir Heister Ryley', attributed to Daniel Defoe and Charles Povey, is established.
The clarinet appears for the first time in an orchestra, in J. A. Hasse's 'Croesus'.
Joseph Addison and Richard Steele publish their influential and popular 'Spectator'.
The 'Free-thinker' is published.
Alexander Pope writes his 'Essay on Criticism'.
Anthony Ashley Cooper, third Earl of Shaftesbury, writes 'Characteristics of Men, Manners, Opinions, and Times'.
Thomas Newcomer patents the atmospheric steam engine, the first significant power source excepting water and wind.
Alexander Pope writes 'The Rape of the Lock'.
The Stamp Act is extended to include newspapers, amid protests from publishers and writers.
Publication of 'Plain Dealer', attributed to William Wagstaff.
Nathaniel Culpepper publishes 'Culpepper Reviv'd'.
The 'Lay-Monk' is established by Richard Blackmore as a sequel to the 'Spectator'.
Publishing run of 'The British Merchant'.
Gabriel David Fahrenheit constructs a mercury thermometer, using the scale that will later be named after him.
George I crowned King of Great Britain. Start of the rule of the House of Brunswick, Hanover line.
Publication of 'The Monitor'.
Male literacy in Britain is around 45%, and female literacy is around 25%, although within the elite literacy is almost 100%.
A school of dance is established at the Paris Opera.
The first Liverpool dock is built.
Publication of 'The Freeholder'.
Publication of 'The Reader'.
Publication of 'The Censor'.
Publication of 'The Original Weekly Journal'.
Publication of 'The Grumbler'.
Publication of 'The Medley'.
Publication of 'The St James's Evening Post'.
Publication of 'The St James's Post'.
Publication of 'The Weekly Remarks and Political Reflections'.
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu writes 'Town Eclogues'.
The Septennial Act sets General Elections to be held every seven years.
Daniel Defoe founds the popular and influential moderate Tory newspaper 'Mercurius Politicus' in 1716. It runs until 1720.
The Bangorian Controversy sparks theological argument within the Church of England.
Susannah Centlivre writes 'A Bold Stoke for a Wife'.
Daniel Defoe starts the 'Whitehall Evening Post' in 1718. It will run until 1800.
The 'Leeds Mercury' is first established.
Daniel Defoe publishes 'Robinson Crusoe'.
Printing run of 'The London Journal'.
Bartolomeo Cristofori invents the pianoforte around this period.
Sir Robert Walpole becomes the first Prime Minister of Great Britain.
The collapse of over-inflated share prices in the South Sea Company causes the South Sea Bubble to burst.
The influential French Rococo artist Antoine Watteau dies at the age of 37.
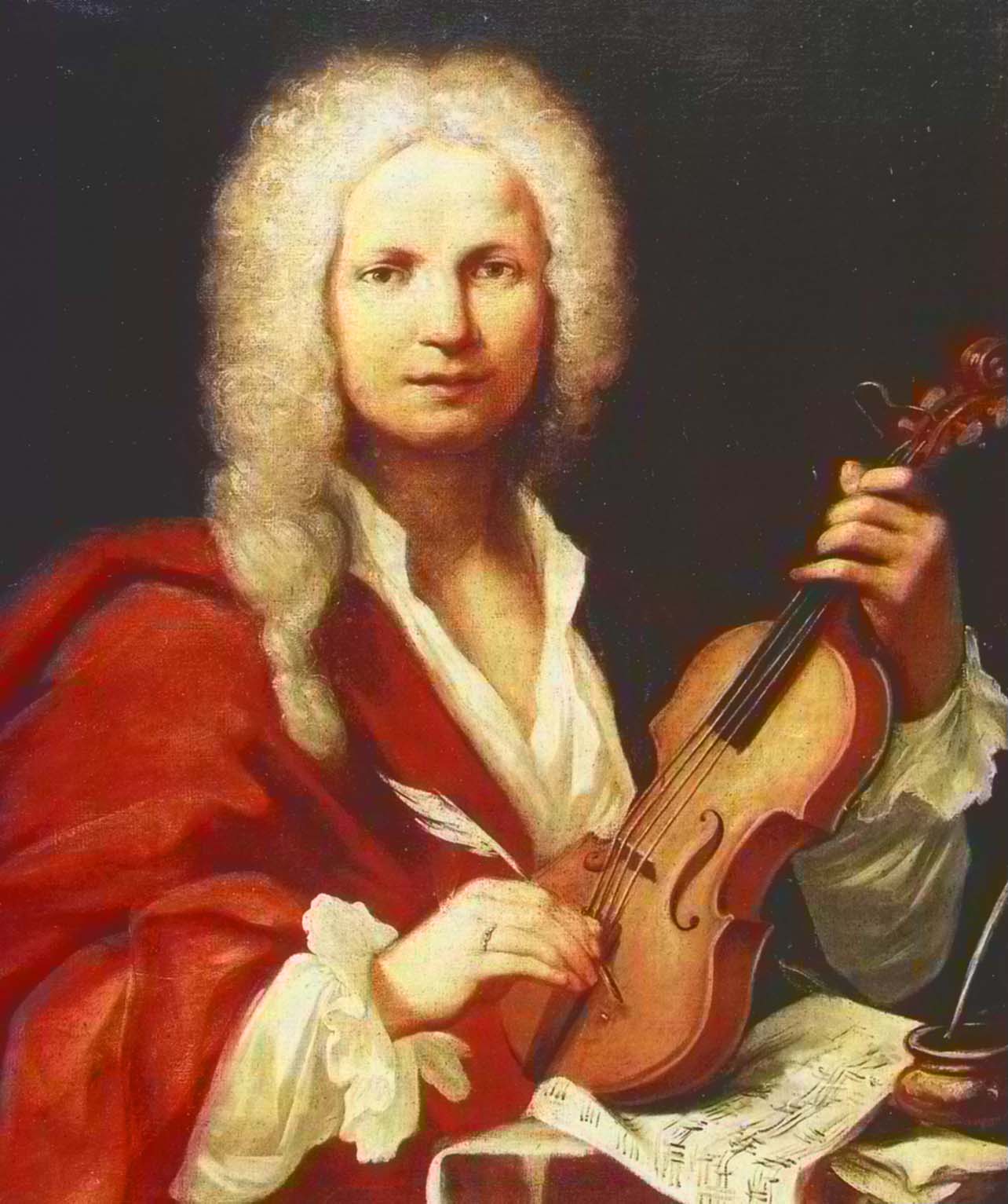

Vivaldi writes 'The Four Seasons'.
The first publication of 'Parker's Penny Post'.
Print run of the 'York Courant'.
George Faulkner establishes the Dublin Journal.
The UK's first circulating library opens in Edinburgh.
Jonathan Swift writes 'Gulliver's Travels'.
J. S. Bach writes his 'St. Matthew Passion'.
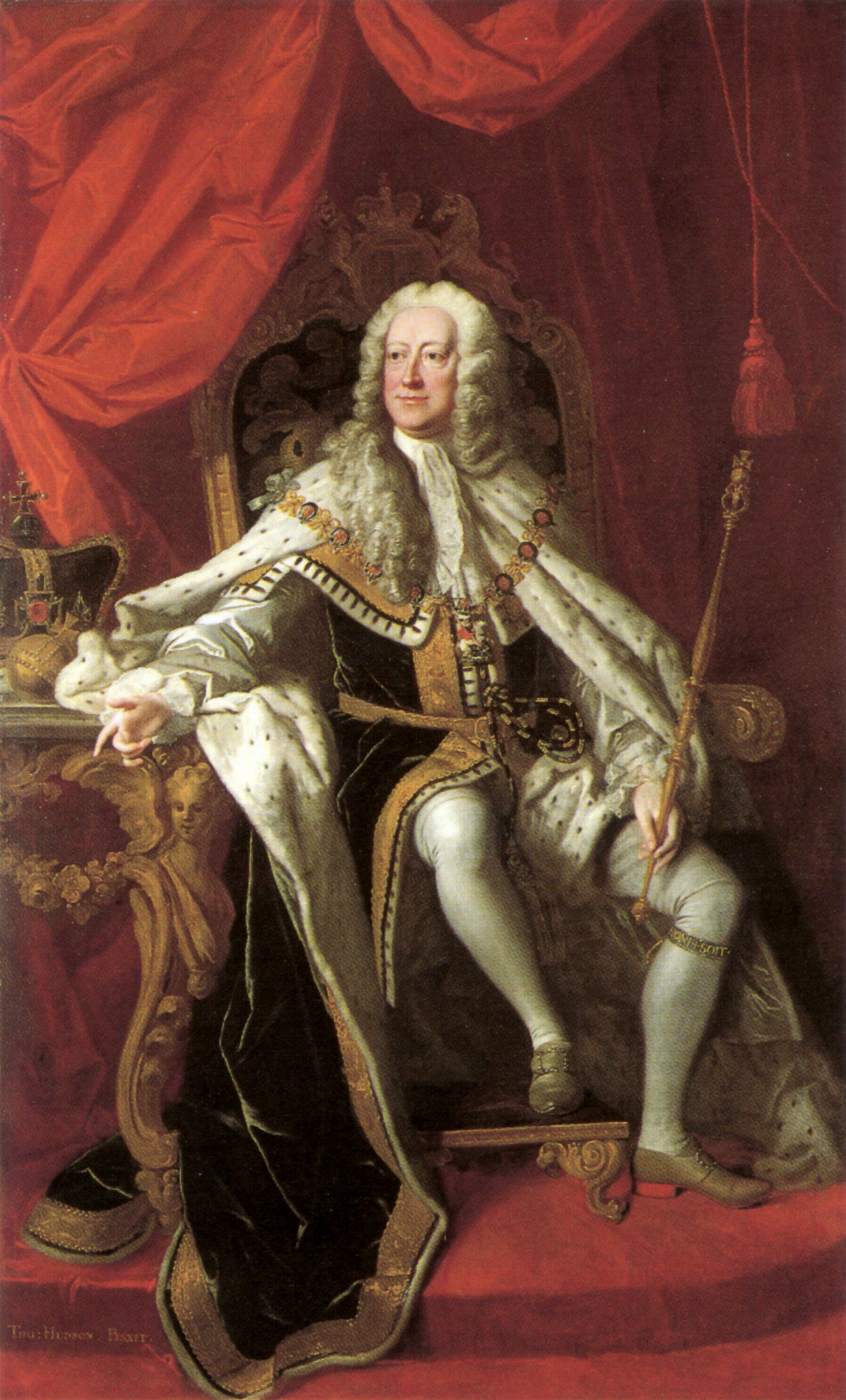

George II is crowned King of Great Britain.
Print run of 'The Present State of the Republick of Letters'.
John Gay writes 'The Beggar's Opera'.
Bernard de Mandeville writes 'The Fable of the Bees, or Private Vices, Public Benefits'.

10 Downing Street becomes the official Westminster residence of British Prime Ministers.
Covent Garden Opera House opens in London.
First publication of Matthias Earbury's 'The Universal Spy; Or, the Royal Oak Journal Reviv'd'.
First publication of the 'Dublin Evening Post'.
Publication of 'B Berington's Evening Post'.
William Hogarth publishes 'A Rake's Tale'.
Beginning of the Welsh Methodist Revival.
Laws against witchcraft formally repealed in Britain.
Philip Mercier, who brought Rococo to Britain, paints 'A Music Party'.
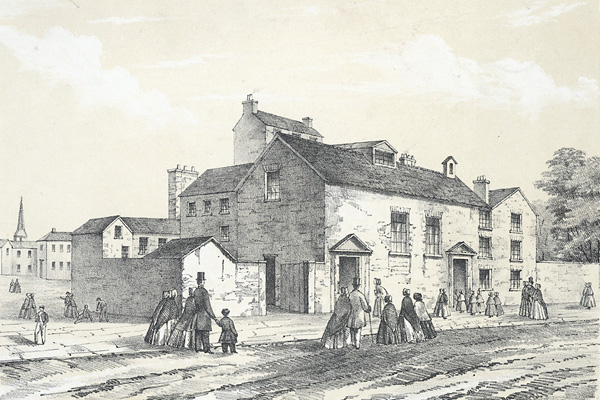

The Methodist Movement begins, led by John and Charles Wesley.
Henry Fielding publishes the 'Champion'.
A survey records 551 coffee houses in London.
David Hume publishes the first part of his 'Treatise of Human Nature'.
Samuel Richardson publishes 'Pamela'.
War of the Austrian Succession.