1740
Samuel Richardson publishes 'Pamela'.
Samuel Richardson publishes 'Pamela'.
War of the Austrian Succession.

Henry Fielding publishes 'An Apology for the Life of Mrs Shamela Andrews'.
First performance of Handel's 'Messiah' at Dublin's Temple Bar.
Ranelagh Pleasure Gardens are opened to the public.
Anders Celsius invents the Celsius scale of temperature.
Edward Young writes 'The Complaint, or Night Thoughts on Life, Death and Immortality.
The Whig politician the Earl of Wilmington becomes Prime Minister.
Selling unstamped newspapers becomes a criminal offence in Britain.
The Whig politician Henry Pelham becomes Prime Minister.
The Thesaurus Musicus publishes 'God Save the Queen'.

Samuel Johnson writes 'Life of Mr Richard Savage'.
The failed Jacobite Rebellion to restore the Stuarts to the throne of Britain is led in Scotland by 'Bonnie Prince Charlie', but is ultimately defeated at the Battle of Culloden by Hanoverian forces.

Print run of 'The Museum; or, the Literary and Historical Register'.
David Garrick becomes actor-manager at the Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, in London.
Samuel Richardson publishes 'Clarissa'.
James Lind discovers that citrus fruits help to prevent scurvy.
Edmund Burke sets up his debating club at Trinity College, Dublin, known as 'Edmund Burke's Club'. It will later become the famous College Historical Society.
Excavation of the ancient Roman site of Pompeii begins.
John Cleland's erotic novel 'Fanny Hill, or, Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure' leads to the author's arrest for "corrupting the King's subjects".
David Hume publishes 'Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding'.
Charles, Baron de Montesquieu, writes 'The Spirit of the Laws'.

Henry Fielding writes 'Tom Jones'.
Peter Bayle publishes 'The Royal Magazine; Or, Quarterly Bee'.
Overall male literacy in Britain has increased to around 60 per cent; female literacy around 40 per cent.
William Hogarth produces Beer Street and Gin Lane at the height of the so-called London Gin Craze. The Gin Act prohibits gin distillers from selling to unlicensed merchants, and restricts retail licenses.
Thomas Gray publishes 'Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard'.
Denis Diderot's Encyclopédie is published. Its eventual 35 volumes will attempt to summarise all human knowledge in every intellectual field.
David Hume publishes 'Enquiry Concerning the Principles of Morals'.
The population of London rises to 650,000. The population of Birmingham rises by 200% to c. 24,000. The population of Leeds rises by 300% to c.28,000.
Carolus Linnaeus writes his 'Philosophica Botanica'.
Benjamin Franklin shows that lightning is a form of electricity through his kite experiment.
Charlotte Lennox publishes 'The Female Quixote, or, The Adventures of Arabella'.
Gregorian calendar reforms are finally implemented in England, bringing the calendar in line with the rest of Europe and Scotland.
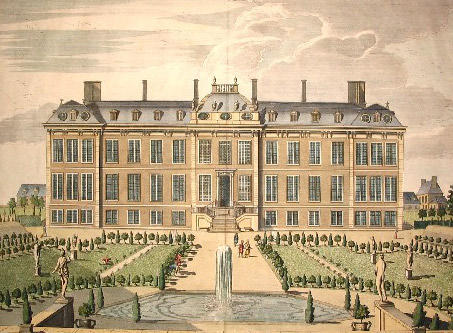
The British Museum is founded.
The Jewish Naturalisation Bill is passed by Parliament.
Isaac Newton publishes 'An Historical Account of Two Noble Corruptions of Scripture'.
Horace Walpole publishes 'The Castle of Otranto', the first Gothic novel.
The Duke of Newcastle, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
Print run of 'The Connoisseur'.
Samuel Johnson publishes his influential book 'A Dictionary of the English Language'.
Johnson's Dictionary defines Grub Street as "a street...in London, much inhabited by writers of small histories, dictionaries, and temporary poems, whence any mean production is called grubstreet."
Owen Ruffhead publishes the 'Contest'.
The Duke of Devonshire, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
The Seven Years War.
The Duke of Newcastle, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister for a second term.
Edmund Burke publishes 'A Philosophical Enquiry into the Sublime and the Beautiful'.
Patrick Delaney establishes the 'Humanist'.
Robert Dodsley, and Edmund Burke, responsible for the 'Annual Register'.
The first subscription library (specialising in serious non-fiction) opens in Liverpool.
Andrew Meikle invents the first threshing machine.

Adam Smith publishes 'The Theory of Moral Sentiments'.
Laurence Sterne publishes 'The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy'.
The Botanical Gardens at Kew are opened.

George III is crowned King of Great Britain.
The 'British Magazine; Or, Monthly Repository for Gentlemen and Ladies' is published.
James Brindley's Bridgewater Canal opens, connecting the Duke of Bridgewater's coal mines in Worsley to Manchester, halving the price of coal in the city.
The 'Universal Museum' is published.
James Macpherson writes 'Fingal, an Ancient Epic Poem'.
The Earl of Bute, a Tory, becomes Prime Minister.
Jean Jacques Rousseau writes 'Emile; Or, On Education and The Social Contract'.
Johann Joachim Winckelmann produces his influential 'History of Ancient Art', which establishes Classical Greece as the pinnacle of artistic achievement and paves the way for Neoclassicism.

George Grenville, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
Mozart performs on the harpsichord at Ranelagh Pleasure Gardens.
Dr Johnson's Literary Club is established on the suggestion of Sir Joshua Reynolds.
Voltaire publishes his 'Dictionnaire Philosophique'.
James Hargreaves invents the spinning jenny, a hand-operated tool for the multiple spinning of wool.
A new Stamp Act is enforced in the American colonies to help pay for the British military presence there. It is met with fierce resistance and adds fuel to the movement for American independence.
The Marquess of Rockingham, a Whig, becomes the Prime Minister.
Sir William Blackstone writes 'Commentaries on the Laws of England'.
Oliver Goldsmith writes 'The Vicar of Wakefield'.

William Pitt 'the Elder', a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
Adam Ferguson writes 'An Essay on the History of Civil Society'.
Astley's Amphitheatre, the first modern circus, is established in London by Philip Astley.
Publication of the 'Political Register', edited by John Almon.
The Royal Academy of Arts is established.
The Duke of Grafton, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
Publication of the 'Encyclopaedia Britannica' begins.
Richard Arkwright patents the 'water' or spinning frame, the first powered textile machine.
Sir Joshua Reynolds paints 'Colonel Acland and Lord Sydney, the Archers'.
David Garrick's play 'The Jubilee', opens at the Theatre Royal, enjoying the longest run of any eighteenth-century theatrical production.
James Watt produces a far more efficient steam engine than the Newcomen model.
Thomas Gainsborough paints 'The Blue Boy'.
The 'Whisperer', edited by William Moore.
Lord North, a Tory, becomes Prime Minister.
James Cook claims the East coast of Australia for George III, naming it New South Wales.
The London firm Flight and Kelly produce the first barrel organs.
The 'London Packet, or New Lloyd's Evening Post' is first published.
Print run of the 'York Chronicle'.
James Watt goes into partnership with Matthew Boulton to commercially produce his steam engines.
The first edition of the Newgate Calendar is published.
The 'Vauxhall Affray' attracts much negative publicity towards the riotous behaviour of visitors to the Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens.
Henry Home, Lord Kames, writes 'Sketches of the History of Man'.
Robert Adam, one of the most successful and fashionable architects of eighteenth-century Britain, builds Osterley Park, London for Child & Co. Bank.
Samuel Johnson and James Boswell write 'A Journey to the Western Islands of Scotland'.
The American War of Independence, also known as the American Revolutionary War.
Thomas Paine writes 'Common Sense'.
Adam Smith writes 'An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'.
Edward Gibbon writes 'The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'.
The Declaration of Independence is signed in America.
Publication of the 'Vocal Magazine'.
Frances Burney writes 'Evelina'.
The 'Political Magazine and Parliamentary, Naval, Military, and Literary Journal' is first published in 1779, with the main print run being 1780-1790.
John Wesley publishes 'Collection of Hymns for the Use of the People Called Methodists'.
Robert Raikes begins the Sunday School Movement.
William Herschel discovers Uranus.
Emmanuel Kant writes 'Critique of Pure Reason'.
The Catholic population of Great Britain is 70,000.
Thomas Gainsborough's 'Giovanna Baccelli' is exhibited. It is an example of British Rococo art.
George Crabbe writes 'The Village'.
Between 27th March and 1st July the Marquess of Rockingham, a Whig, is Prime Minister for a second term, but he dies in office. On the 4th July the Earl of Shelburne, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister.
Richard Arkwright begins using Boulton and Watts' steam engines in his textile factories.
On 2nd April the Duke of Portland, a Whig, becomes Prime Minister. On 19th December William Pitt 'the Younger', a Tory, takes over as Prime Minister.
John Wesley issues the 'Deed of Declaration', outlining rules and regulations for the guidance of Methodists.
The India Act establishes a parliamentary Board of Control to oversee the East India Company.
Arthur Young publishes 'The Annals of Agriculture'.
John Pendred publishes the first guide to English publishing, 'The London and Country Printers, Booksellers and Stationers Vade Mecum'.
Edmund Cartwright patents the first power loom.
Sibbald's Library in Edinburgh offers over 6,000 titles to patrons.
Robert Burns writes 'Poems, chiefly in the Scottish Dialect'.

The US Constitution is completed.
Mozart's opera 'Don Giovanni' is premiered in Prague.
Publication of the 'Dublin Chronicle'.
The Times, Britain's oldest surviving newspaper, is created.
Sir John Soane is appointed architect and surveyor to the Bank of England, the exterior of which becomes his most famous work.
The 'First Fleet' of around 1,400 convicts, arrive in Botany Bay, Australia.
William Blake writes 'Songs of Innocence'.
The French Revolution begins.
The dechristianisation of France during the French Revolution begins.
Jeremy Bentham writes 'Introduction to the Principles of Morals and Legislation'.
Publication of The 'Bee; Or, Literary Weekly Intelligencer'.
Edmund Burke writes his 'Reflections on the Revolution in France'.
The 'Establishment' clause is the First Amendment of the US Constitution. It forbids the establishment of a state religion.
Thomas Paine writes 'The Rights of Man'.
Benjamin Franklin's autobiography is published a year after his death.
The waltz becomes a fashionable dance in England.
Thomas Sheraton publishes 'The Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer's Drawing Book', which influences the development of a neoclassical style of furniture.

Mary Wollstonecraft writes 'A Vindication of the Rights of Women'.
William Godwin writes 'Enquiry Concerning Political Justice and its Influence on Modern Morals and Manners'.
Louis XVI of France is guillotined.
French Revolutionary Wars.
The Louvre Museum opens in Paris.
Publication of the 'Morning Advertiser'.
Publication of the 'Morning Post and Fashionable World'.
Ann Radcliffe, the most successful novelist of the century, publishes 'The Mysteries of Udolpho', which sets the standard for Gothic fiction.
Thomas Paine writes 'The Age of Reason'.
Erasmus Darwin publishes 'Zoonomia'.
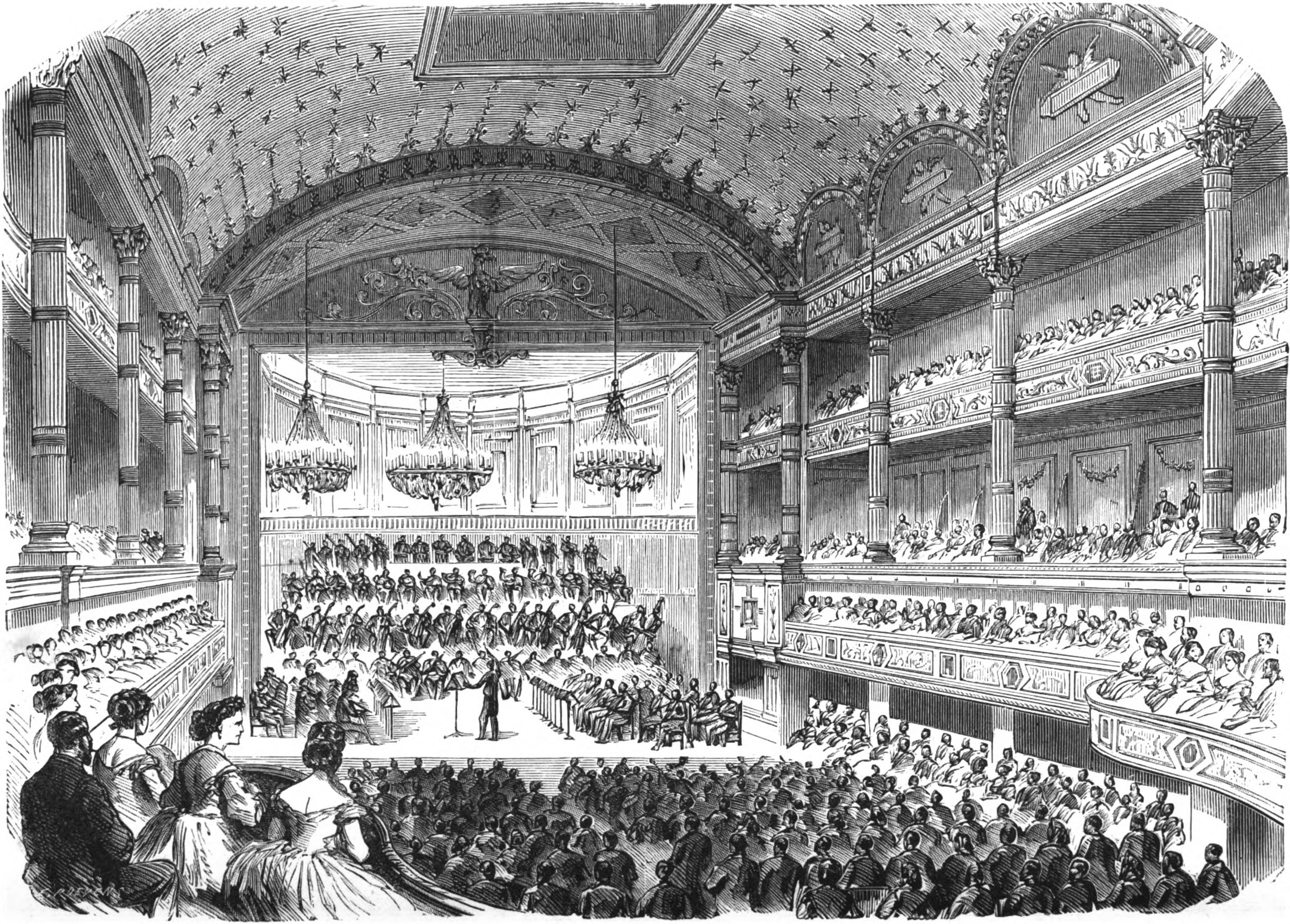
The Paris Conservatoire de Musique is established.
Edward Jenner performs an inoculation against Smallpox using Cowpox for the first time.
Matthew Lewis publishes his early Gothic novel 'The Monk'. Its sensational content provokes an attempted legal action to protect public morality, but this merely adds to its popular success.
J. M. W. Turner exhibits his first work at the Royal Academy, 'Fishermen at Sea'.
Thomas Malthus writes 'An Essay on the Principle of Population'.
William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge publish their 'Lyrical Ballads', marking the beginning of the Romantic movement in literature.
Print run of the Oeconomist.
The Rosetta Stone is found, aiding the interpretation of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs.
By the end of the century there are over 1,000 libraries in Britain.
First publication of Mungo Park's 'Travels in the Interior Districts of Africa...in the Years 1795, 1796 and 1797'.
Napoleon is appointed First Consul of France.
The Church Missionary Society is founded.
40% of Britain's population earn their living from the land.